A summary of the #LearnSEO Twitter chat where Olaf Kopp and Marie Haynes discuss E-A-T and semantic search in Google’s algorithms.
In this chat we discussed the following topics:
- How does Google evaluate authors as entities?
- What is the connection between E-A-T and the idea of a “brand”?
- How to use knowledge graph tools to write better author bios.
- How Hummingbird changed search to give Google semantic search capabilities (and why this is a big deal.)
- How we can determine which entities are associated with our brand, and what we can do with that information.
About Olaf Kopp

Olaf Kopp is Co-Founder, Chief Business Development Officer, and Head of SEO at the German online marketing agency Aufgesang GmbH. He is an author, podcaster, and industry expert in semantic SEO, E-A-T, online & content marketing strategies, and digital branding. He has published incredible stuff on E-A-T and semantic search over at Kopp Online Marketing Consulting & Aufgesang (German only).
About Marie Haynes

Marie is the founder of MHC, a digital marketing agency that specializes in understanding and improving website quality in Google’s eyes. MHC is known for their work on improving E-A-T and all other aspects of site quality.
How is author E-A-T evaluated by Google’s algorithms?
Marie: Let’s talk about author E-A-T! Here are a few examples of how quality raters are instructed to evaluate the E-A-T of authors. Google’s algorithms likely evaluate authors as entities. Olaf, can you explain more on this?




Olaf: Google organizes in semantic databases like the knowledge graph attribute value pairs, related sub entities, entity types, digital representations of the entities and related content around the entities. Here is an example:
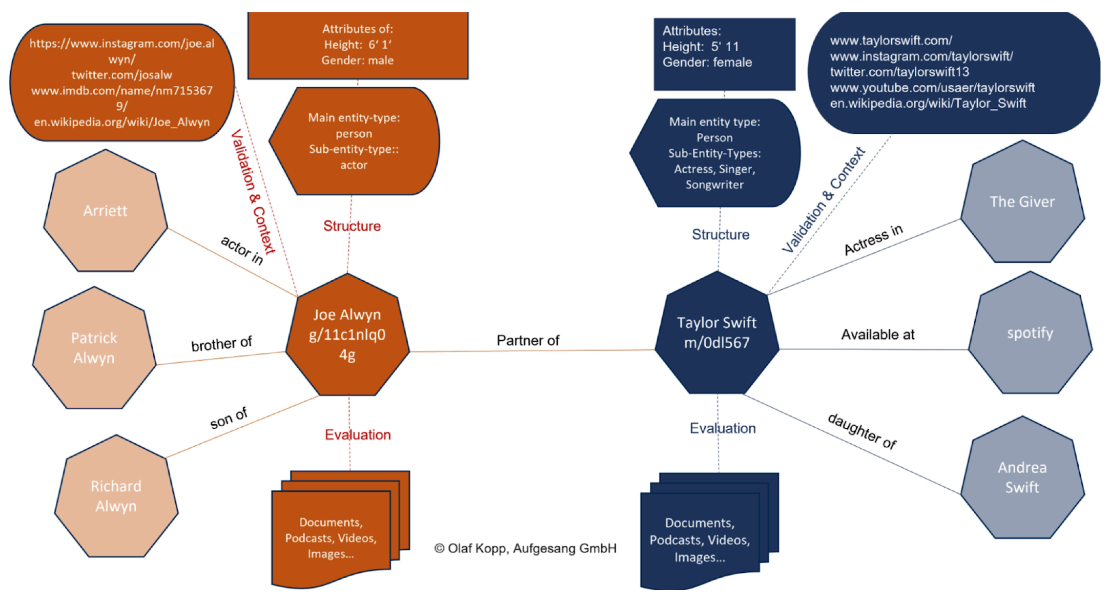
Google can draw conclusions about E-A-T of an entity of the content via the respective entity. Google can determine an expertise via the digital representations such as social media profiles, author profiles, speaker profiles and representations of the entities.
Authority and trust can be statistically determined via content, references (PageRank) and other signals from third-party media. I summarized possible signals in this article.
The development of semantic search and E-A-T are closely linked, because Google can evaluate authors, publishers, organizations … as entities using statistical methods in terms of expertise, authority and trust.
How having a “brand” relates to E-A-T
Marie: Google tells us that assessing your own content from an E-A-T perspective can help us rank better. The QRG says E-A-T considers the expertise of the creator of the content, but also more.
Olaf, can you discuss your thoughts on the importance of the idea of a brand?
I asked this question because Olaf’s writing explains that the concept of a brand encompasses E-A-T. When you think of a brand, you think of characteristics like popularity, authority and reputation.
Matt Cutts told us years ago that Google doesn’t recognize businesses as brands, but rather they use words like “trust”, “authority”, “reputation”, “PageRank” and “high quality”.
Olaf: With the E-A-T concept, Google tries to understand entities as brands, especially with regard to thematic positioning. I think popularity (for example search volume for exact brand keywords) is not that important as it gives no indication of any thematic context.
Co-occurrences in search queries and content between brand keywords and thematically relevant keywords are more interesting to learn more about the brand and its thematic positioning. More in this article.
Danny Sullivan has denied the connection between Brand and E-A-T. Besides popularity, expertise, authority and trust are the most important characteristics of a brand.
Marie: My goal here is not to get people saying that being a big brand is a ranking factor. Rather, I’m encouraging you to look at how people think of your business. In the Quality Raters’ Guidelines, Google instructs the raters that there are different ways to look at the reputation of a business depending on the purpose of that business. Popularity may be important.

Using knowledge graph tools to write better author bios
Marie: The knowledge graph records entities and the relationships between them. This tool – the DiffBot NLP demo, is blowing my mind. It shows how entity information is stored in the kg.
This next question is a little embarrassing for me…
I put Olaf’s bio and my bio into the tool. You can see that Olaf’s is very well written in a way that entity information can be extracted. Mine is clearly not! (I do not work for Google😂)
Olaf, how would I go about improving my bio? Why should I do that?
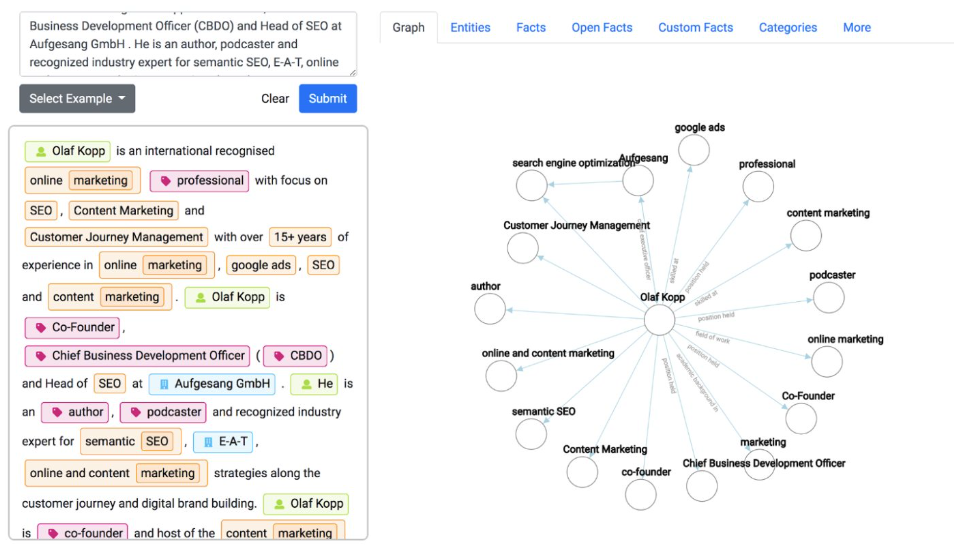
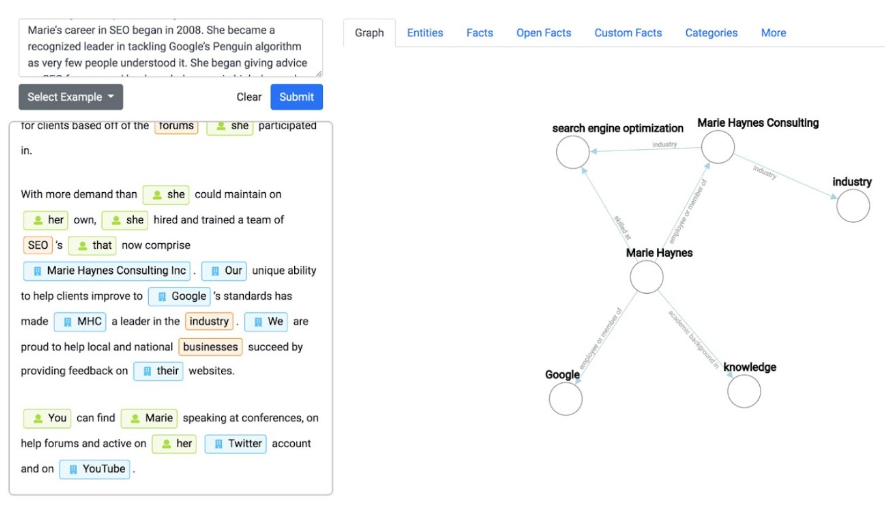
Olaf: Note that Google can easily recognize triples in the form of subject, predicate, and object triples. I also think it makes sense not to use too many adjectives and adverbs, as they can complicate the extraction of triples and thus the machine understanding.
For example, you should pay attention to a simple sentence structure so that Google can easily determine the relationships to sub-entities, attributes… This also makes the text easier to read for the user.
If you understand how natural language processing works, you can deduce how to create texts for entities.
How Hummingbird changed Google’s search algorithms
Marie: How did Hummingbird, launched in 2013, change Google’s search algorithms?
Olaf: The launch of Hummingbird marked finally the start of semantic search. Google itself has called this algorithm update one of the most significant updates in Google history. However, the effects of Hummingbird are gradual, unlike the core updates.
With the Knowledge Graph, Google introduced an entity-based index. With Hummingbird, Google supplements the keyword-based ranking with an entity-based ranking.
Both methods are still running in parallel to this day, but I think entity-based ranking will become more and more popular. Rankbrain, BERT and MUM have been introduced for better understanding of documents and search queries.
With the introduction of Natural Language Processing Google Search will become more and more semantic because named entity recognition and semantic data mining is becoming more and more scalable.More here on using NLP to build a semantic database.
Marie: I’ve been learning a lot about semantic search lately. Here’s a long tweet thread where I lay out my thoughts:
#LearnSEO is going to be different this week. Here's a long thread with my thoughts on
➡️entities
➡️semantic search
➡️E-A-T
➡️content qualityThere will be some questions in the thread, but this isn’t a typical Q1/A1 chat.
— Marie Haynes (@Marie_Haynes) April 20, 2022
And here’s a Youtube video version of my podcast where I expand on this even further:
How to determine which entities Google associates with your brand
Marie: How can we determine which entities Google thinks are related to our brand? Why is this important?
Olaf: The terms that are often used to search for your own brand show Google and us what our brand stands for. Also you can use keyword planner beginning with the domain. Then you will get a list of keywords ranked by relevance.
It could be that E-A-T plays a role in indexing and the number of results you get for a keyword in SERPs. In general, one can say:the more space Google grants me in the SERPs, the more credible one seems to be as a source to a specific topic and keyword. cluster.
So you can identify thematic keyword clusters with top rankings, double rankings and rich snippets (stars, FAQs…). You can analyze the brand and navigational keywords e.g. via the search console, keyword planner, related search queries and suggest.
Marie: This was a great tip. You can use Google Ads’ Keyword planner to get clues on what entities are associated with your brand. If they’re not right, it’s probably a good idea to change up the copy.
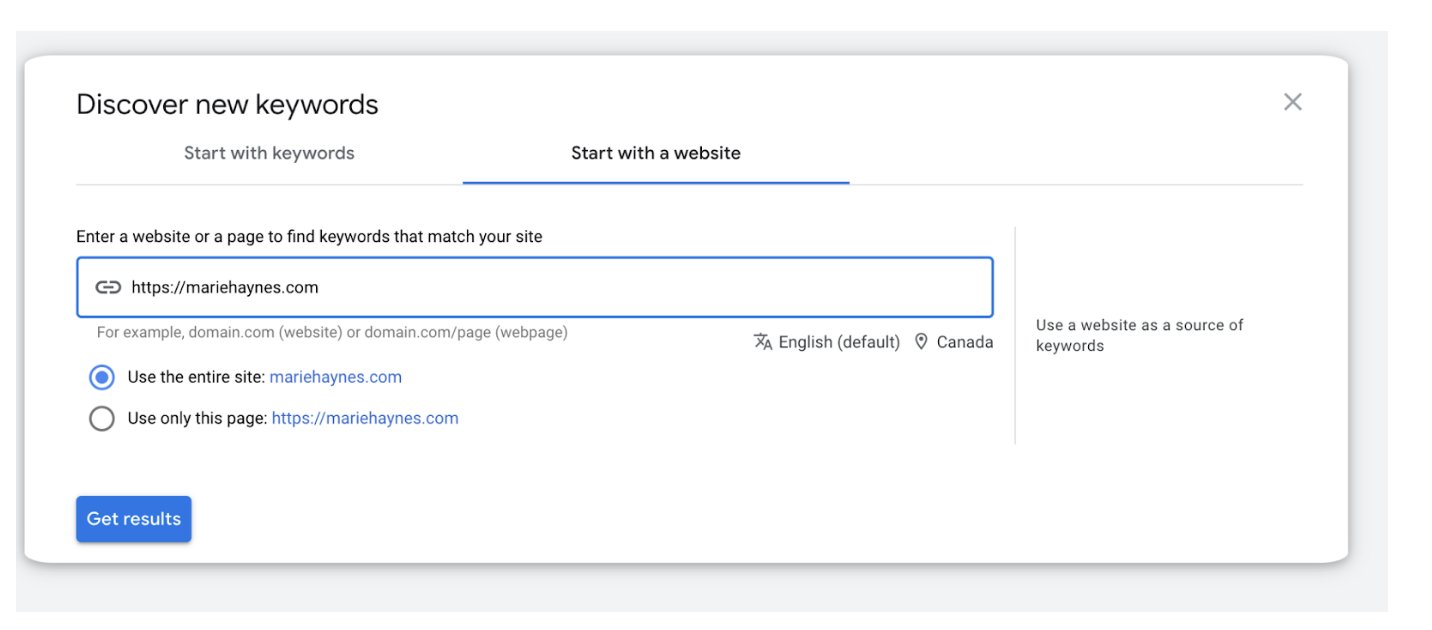
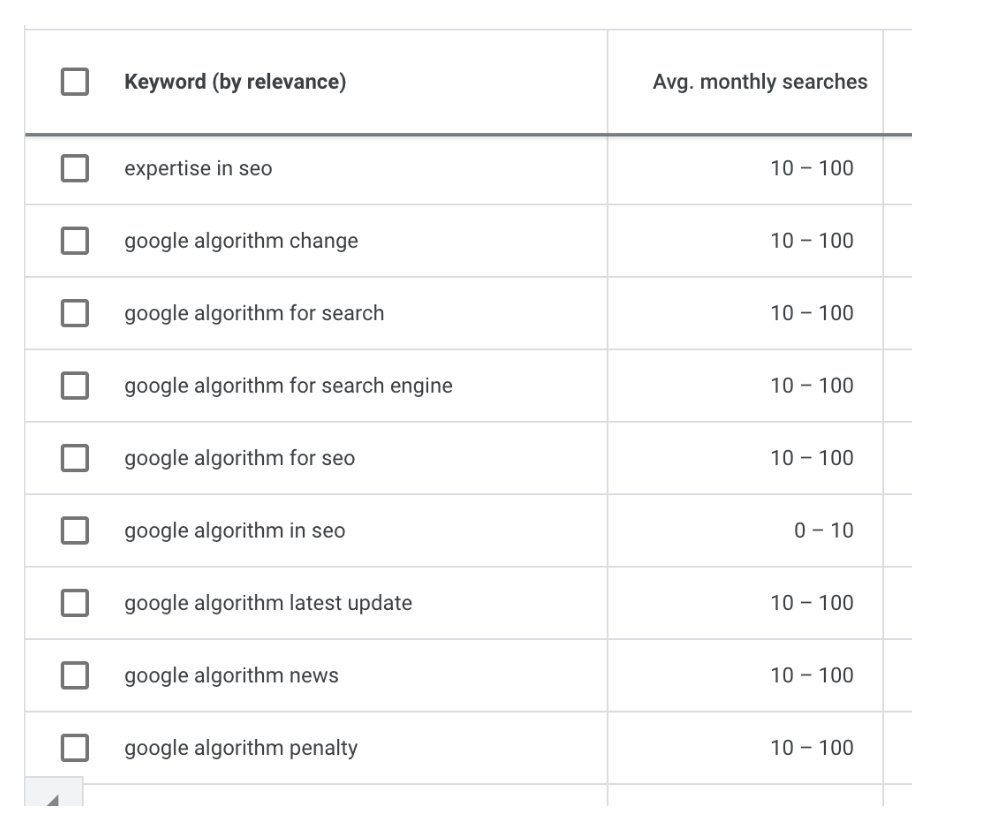
In addition, I believe in an influence on the delivery of rich snippet elements such as stars or FAQs. You need a certain “Quality Threshold” to get them. Don’t get me wrong, I’m not talking about an E-A-T score, which according to Google doesn’t exist.
The relationship between entities google can identify by triples and/or co-occurrences. I think E-A-T has more impact on Google searches than rankings. Google has confirmed that E-A-T also has an important impact on delivery on Google Discover and Google News.
Thank you to Olaf for chatting! You’ll get to see and hear him shortly when I interview him on podcast next week so we can discuss E-A-T and semantic SEO even further.
Follow us on Twitter to join us for the next edition of #LearnSEO!


Comments
Thanks