Google says every enterprise will soon rely on multi-agent systems - multiple AI agents working together.
That sounds exciting and futuristic, but what I’ve found when talking to my clients is that while agents sound like something we should all be building, there’s little information to help you decide what your business should be doing right now.
Let me share an example of a complex enterprise that is currently doing cool things with AI agents. Then, we’ll get into what agents are and I’ll hopefully help you decide whether you should be investing in this technology.
- Agents are autonomous problem-solvers: Unlike simple chatbots, AI agents can make decisions, learn, use tools (MCP), and collaborate (A2A) to achieve complex goals.
- Walmart is a real-world example: Their use of specialized agents (Sparky for customers, associates for internal ops, digital twins for store testing) demonstrates agents' power in interconnected workflows.
- Google is building the agentic web: With "AI Mode," "Gemini in Chrome" using tools like Project Mariner, and the Agent Payments Protocol (AP2), Google is laying the groundwork for agents to perform tasks and manage transactions online.
- Agents will disrupt search and the economy: This shift promises to automate mundane tasks, redefine web interaction, and create new economic opportunities as agents interact and negotiate.
- Prepare proactively, don't wait: While full-scale agent deployment might be nascent for most, foundational steps taken today are vital.
An example of agents working together in a business
Walmart uses a number of AI agents. Each of them is designed for highly specific tasks. First, there’s Sparky. At first glance Sparky looks like a regular chatbot.
But it does more than just chat. It connects with inventory, suggests products, and can even suggest recipes and add the missing ingredients to your cart.
Walmart CTO Hari Vasudev said that this type of interface could be the future of how people search: "
“We expect that the search bar and the conventional way of searching for items will be replaced by this multimodal interface in Sparky."
Where it really gets interesting is when you see how Sparky works with Walmart's other agents. They say,
“Extensive early testing proved that, for us, agents work best when deployed for highly specific tasks, to produce outputs that can then be stitched together to orchestrate and solve complex workflows.”
This stitching together of AI driven workflows is what makes me excited about how agents will transform the way we do business.
Walmart has other AI agents including one built for their associates that helps them find things in the store and deal with HR questions and other operational issues and another called "Marty" which works with suppliers and sellers to help manage onboarding, orders and advertising campaigns.
What’s most interesting to me is the system of agents Walmart uses to create a digital twins. They make virtual 3d models of their stores and then use these digital twins to test things like store layouts and run what-if scenarios. Then, the associate agent could connect with that agent to get real time guidance on restocking. Or, and here’s the part I think is wild…the digital twin of a store might notice that a refrigeration unit is likely to break down. It can then send a message to a repair technician in that store along with the parts they need and an instruction manual on what needs to be done.
Walmart uses Model Context Protocol (MCP) to standardize how many agents interact with the services they already have.
I can see the tremendous value in what Walmart is doing, but how do we translate that into ideas that I can truly implement in my own business or recommend for my clients? It's all so overwhelming!
Before we go further, let’s get some basics covered.
What are AI Agents?
Google's definition of agents is that they are software systems that use AI to pursue goals and complete tasks. They can use reasoning, planning, and memory and they can have a level of autonomy, working on their own, to make decisions, learn and adapt.
An AI Chatbot generally follows a script. An Assistant uses AI to provide personalized help. An Agent, on the other hand, can work proactively, use tools, and even work with other agents, sometimes autonomously, to achieve complex goals.
| Feature | AI Agent | AI Assistant | Simple AI Chatbot |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | High. Can operate independently to achieve a goal. | Medium. Assists users but decisions are made by the user. | Low. Follows pre-programmed rules. |
| Complexity | Handles complex, multi-step tasks and workflows. | Completes simple, single-step tasks. | Automates basic, simple conversations. |
| Interaction | Proactive and goal-oriented. | Reactive, responds to user requests. | Reactive, responds to specific triggers. |
| Learning | Can learn from experience and adapt its behavior. | May have limited learning capabilities. | Limited to no learning based on interaction. |
I think of an AI Agent like an employee. You can train them to do things, to use tools. You give them a goal to accomplish and they have some autonomy to determine the best way to do that. And also, if they’re good, they’ll keep learning and improving.
Agents start with an LLM - your agent may use ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, Grok or any other LLM. They can connect with tools via something called Model Context Protocol, MCP. Think of MCP like a universal connector that makes it so that any LLM can work with a tool. The tool is essentially something you could use programmatically via an API. For example, Google Search, Google Search Console, or maybe Stripe. The difference between an MCP and an API is that with MCP the LLM doesn’t need to know the specific code to use for each individual tool - it just needs to describe what it wants to do with the tool.
In short, MCP allows agents to speak with tools.
Now, communicating with tools is one thing, but what we really need to grasp is what happens when agents communicate with other agents. Google made a protocol for this - similar to how we have a protocol for http, called A2A - Agent to Agent.
Agent to Agent communication
With A2A every agent has a card that uses a simple language called JSON to describe what it can do.
Here is an example from Google:

The Agent Card might look like this:
# A2A Agent Skill definition
skill = AgentSkill(
id='get_exchange_rate',
name='Currency Exchange Rates Tool',
description='Helps with exchange values between various currencies',
tags=['currency conversion', 'currency exchange'],
examples=['What is exchange rate between USD and GBP?'],
)
# A2A Agent Card definition
agent_card = AgentCard(
name='Currency Agent',
description='Helps with exchange rates for currencies',
url=f'http://{host}:{port}/',
version='1.0.0',
defaultInputModes=["text"],
defaultOutputModes=["text"],
capabilities=AgentCapabilities(streaming=True),
skills=[skill],
)
That agent might be a part of a group of agents that can speak with each other.
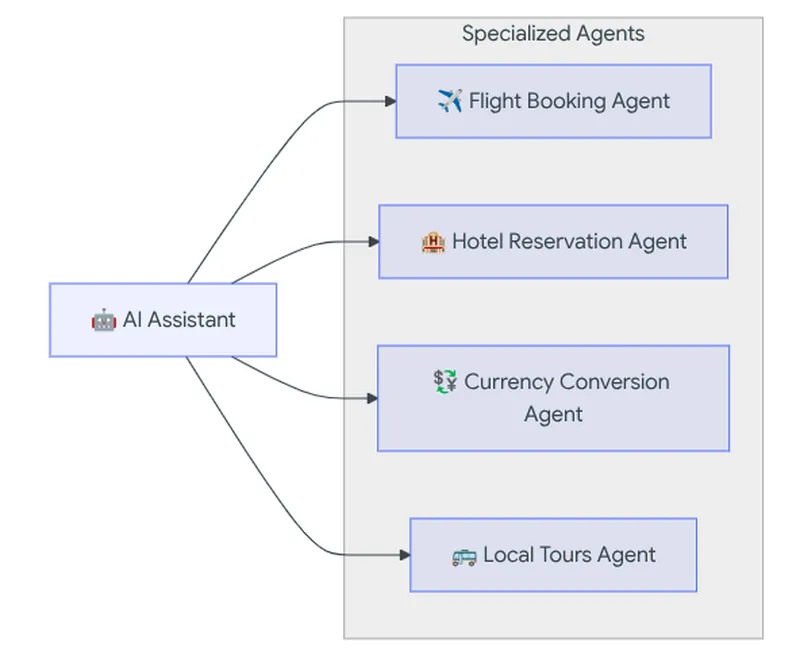
In this example, if this travel agent is talking to a customer and determines that they are asking about booking a hotel, then it can reach out to the hotel reservation agent, and so on.
How will agents be found?
In some cases we will just give our agents a list of agents that they can communicate with. But in other cases, Google’s documentation tells us that the agent can pull from catalogs or registries of agents.
Google does have a marketplace for agents. At the time of writing this, there are 945 agents listed. However, it’s not very straightforward from what I can see. Some of the agents have a cost - but the documentation simply says, to connect with sales for more information on pricing. I think we will eventually see catalogues of agents we can connect with. Or, eventually, I expect that we’ll simply be able to advertise them on our website and LLMs will find them.
Some agents likely will be surfaced in Search.
Google is becoming agentic
Glenn Gabe just posted that he got access to agentic capabilities via AI Mode. It’s pretty primitive right now, but you can see which restaurants have reservations and what time.
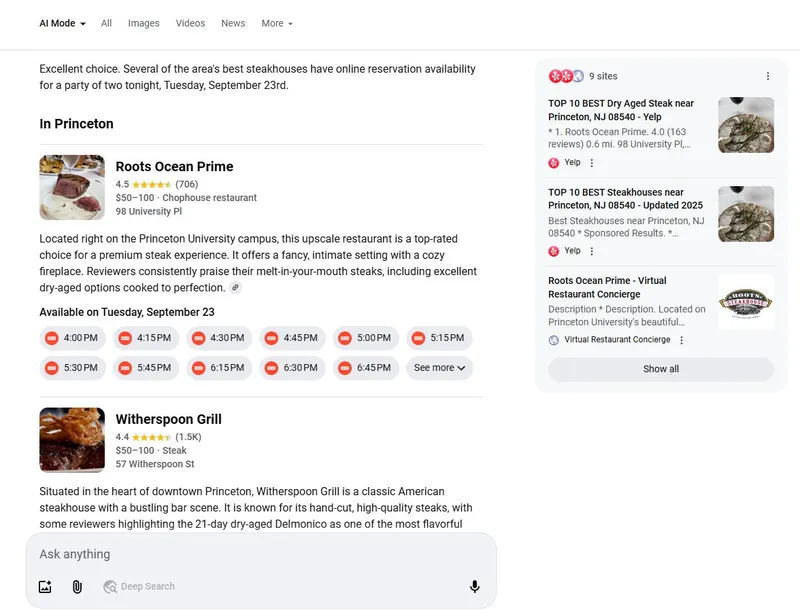
Those restaurants did not need to create agents to be surfaced in AI mode. Rather, those restaurants used a third party booking system that connects with something google created called “reserve with Google”.
At Google I/O we saw the introduction of agents that will help you find tickets by connecting with sites like Ticketmaster and Stubhub right from the Search results in AI Mode. Google is doing the searching for us, assembling information to help us make our decision.
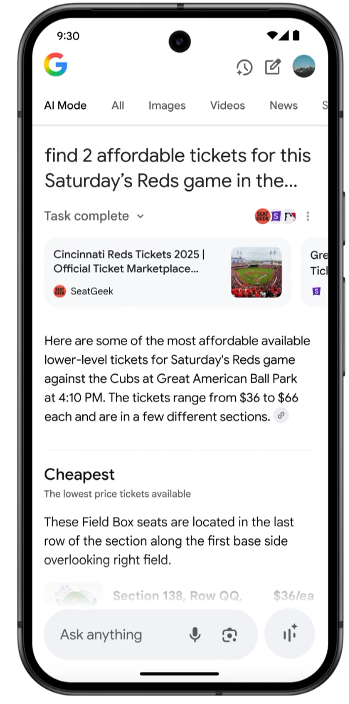
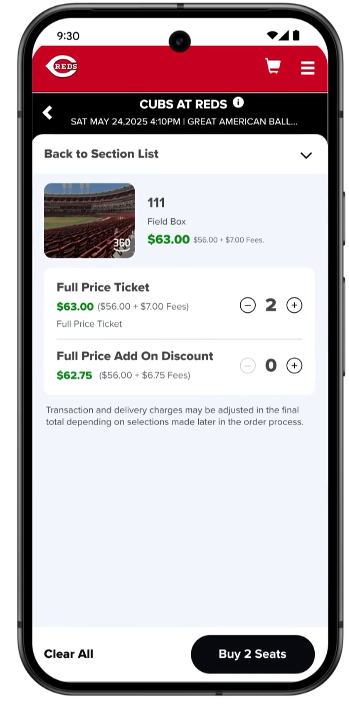
AI Mode can then act as our agent and allow us to purchase right from the search results, without having to visit a website.
Not only will we find agents via AI Mode, we will also have the ability to have Gemini act as our agent from within a Chrome browser. Google recently announced Gemini in Chrome, saying, "Get ready for your agentic browsing assistant." They shared this example where our agent, Gemini in Chrome reads a list from Gmail, and then goes to a website to put grocery items in a cart.
From what I can see, Instacart is not using an agent here. Rather, Gemini is using Project Mariner which is AI using its own Chrome browser to simply search the web and interact with websites.
I think that most websites will not need to do much to become a part of the agentic web, other than make sure your website is easy to use by agentic tools like Project Mariner. This is something I’d recommend doing right now - use ChatGPT Agent and Project Mariner and watch them accomplish tasks on your site.
Agents will eventually handle payments
Google announced a new protocol that will allow agents to handle payments called Agent Payments Protocol (AP2). They have collaborated with Mastercard, American Express, Coinbase, Etsy, Salesforce and Paypal. This protocol will open doors for agents to securely complete payments. Currently this protocol works with common payment methods, but it also is set up to work with cryptocurrency. Also this month, Stripe introduced a new blockchain infrastructure called Tempo. And also, ChatGPT introduced agentic shopping in partnership with Shopify and Etsy.
As agents develop, these protocols will create the infrastructure needed for agents to transfer monetary value. I think the day will come where perhaps you hire my SEO agents on a contract that has you pay me based on whether my agents have helped you make money or improve your efficiency. I think the way that our economy works is going to change significantly.
Will agents replace Search?
I personally believe that agentic use of the web will replace traditional search. Here’s what Google deep mind’s CEO Demi Hassabis says…
“I think there’s going to be a very interesting phase in the next few years on the web and the way we interact with websites and apps and so on. If everything becomes more agent based, then I think we’re going to want our assistants and our agents to do a lot of the work and a lot of the mundane work that we currently do, right? You know, fill in forms, make payments, book tables, this kind of thing.
I think that we’re going to end up with a kind of economics model where agents talk to other agents and negotiate things between themselves and then give you back the results. And you’ll have the service providers with agents as well that are offering services and maybe there’s some bidding and cost and things like that involved and efficiency and then I hope from the user’s perspective, you have this assistant that’s super capable that you can… just like a brilliant human assistant and can take care of a lot of the mundane things for you.
And I think if you follow that through that does imply a lot of changes to the structure of the web and the way we currently use it…I think there will be incredible opportunities that will appear, economic and otherwise, based on this change, but I think it’s going to be a big disruption.”
What I’ve shared so far, is somewhat disruptive, but let’s take things further. It’s one thing for Google to use our websites agentically - for Gemini in Chrome or ChatGPT agent to use the web and do stuff for us. But where things really get crazy is when we have agents that work with other agents.
I have a suite of agents that help me brainstorm on content writing. One agent thinks up ways to use my client’s experience and create original, insightful content. Another finds new research that we might want to write about for our audience. Those are cool…but right now these are like individual employees that are all working on their own. What happens when we have a team of agents?
I might have an agent that uses MCP to connect with Google Search Console and GA4. And that agent can send info to an agent whose job is to analyze pages that are doing well and find what characteristics they have in common. And that agent would connect with a brainstorming agent that I can call on when writing new content. Or, let’s say I’m selling products. I could have agents that brainstorm together on what is working to convert people into customers. Eventually, as we figure out how to do this I could essentially have thousands of agents all working together with one goal - to make my business more successful.
Bit by bit I'm learning to build these systems. Eventually the tech will get easier and I do believe that whatever we can conceive, we will be able to bring to life.
My recommendations for businesses right now
Here’s what I’d recommend.
- Spend every day using an LLM - I’d stick to the well known ones - Gemini, ChatGPT, possibly Claude and Grok. It’s probably good to get used to using multiple language models. Push their capabilities to try and get them to help you do things in your work. Your goal is not to create a full agentic system that transforms your business, but rather, to learn the language of talking to these models. They essentially are just math that is used to make predictions based on the knowledge they have - and the more we learn to benefit from these tools the better. If you have a business, I’d recommend that every employee is tasked with learning something new that they can do with an LLM every week.
- Create Gemini gems every day. These things are awesome. A Gemini Gem is simply a prompt that you reuse regularly. It can have information in a knowledge base that it draws upon. I use gems repeatedly in my day. I expect, but I don’t know for certain, that Google will eventually make it easy for us to turn our gems into agents that can communicate. If you are an enterprise with over 100 seats, you already have something like this via AgentSpace. From what I can see though Agentspace can be expensive. The idea is that any employee can create an agent that works with company data. Personally whenever I have a prompt that I use repeatedly, I make a gem out of it.
- Consider learning to code. You’ve likely heard of vibe coding - coding with natural language. I am not encouraging you to vibe code an app you’re going to sell to the public, but instead, learn to create something that you can use. I made an RSS feed reader which is just awesome and it saves me time. Then I learned how to connect that tool to my Google Docs so I can summarize stories and save them to my newsletter. Bit by bit, I am learning how to code things. I think that those who can code will have endless opportunity to create. I’d encourage you to play with OpenAI’s Codex and also with AI Studio’s build feature. These tools will both get better and allow non-coders to create things. If you start learning now, you’ll eventually be able to build anything.
- Test your website with agentic browsers like Project Mariner and ChatGPT Agent. Make sure your content is accessible to AI and that AI can accomplish things a user would want such as filling out forms or putting products in the cart.
- Stay up to date with how agents are being used in your field. I actually do not think it’s time yet for my clients to build functioning agents that will transform their business. Why? Because the technology is changing rapidly. I think every developer should be playing with Google’s Agent Development Kit and seeing what they can make with it. And I think we should be watching for every new bit of news that helps us understand this tech more. I do think Google will make it easier, but it is going to take some time.
This is probably a good place to mention my newsletter
I spend hours each day reading and learning about how AI is changing our world so I can share it with subscribers of AI News You Can Use.
New - My monthly report on the agentic web
If you're a Search Bar Pro member, click here for a 25% off discount code. If you're not a member of my community, check it out!
We have so much to learn when it comes to agents. Right now, I think we should all be learning and paying attention and understanding how to build and use AI agents. I think that once people start making real money with agents, we will see this field suddenly take off. Let's see!
Marie


 “I think there’s going to be a very interesting phase in the next few years on the web and the way we interact with websites and apps and so on. If everything becomes more agent based, then I think we’re going to want our assistants and our agents to do a lot of the work and a lot of the mundane work that we currently do, right? You know, fill in forms, make payments, book tables, this kind of thing.
“I think there’s going to be a very interesting phase in the next few years on the web and the way we interact with websites and apps and so on. If everything becomes more agent based, then I think we’re going to want our assistants and our agents to do a lot of the work and a lot of the mundane work that we currently do, right? You know, fill in forms, make payments, book tables, this kind of thing.

Comments are closed.